

#JAMES WEBB TELESCOPE LOCATION FULL#
Here, Webb’s powerful infrared eyes bring a second dying star into full view for the first time. Southern Ring Nebula: This planetary nebula, an expanding cloud of gas that surrounds a dying star, is approximately 2,000 light-years away.With Webb’s first detection of water in the atmosphere of an exoplanet, it will now set out to study hundreds of other systems to understand what other planetary atmospheres are made of. WASP-96b (spectrum): Webb’s detailed observation of this hot, puffy planet outside our solar system reveals the clear signature of water, along with evidence of haze and clouds that previous studies of this planet did not detect.This image only scratches the surface of Webb’s capabilities in studying deep fields and tracing galaxies back to the beginning of cosmic time.
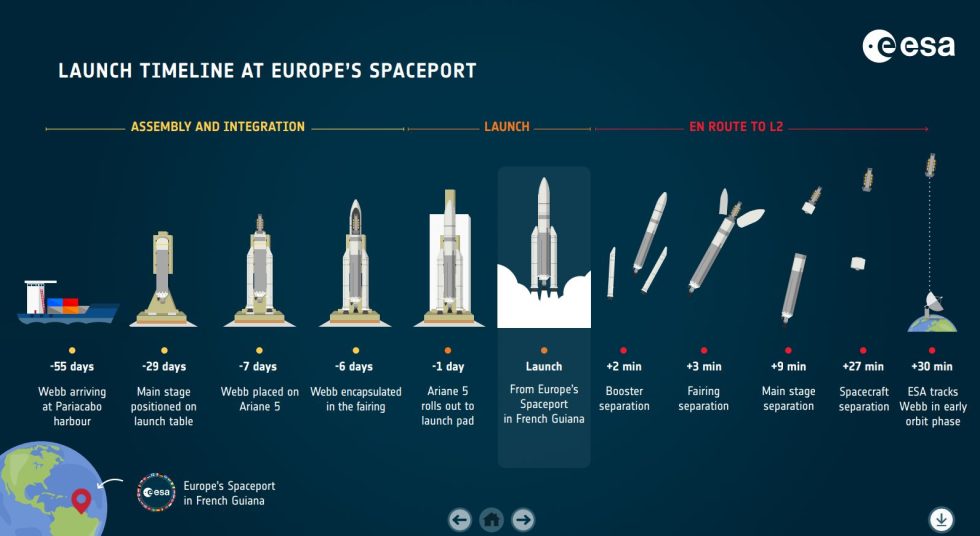
This deep field uses a lensing galaxy cluster to find some of the most distant galaxies ever detected. For a person standing on Earth looking up, the field of view for this new image, a color composite of multiple exposures each about two hours long, is approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length. SMACS 0723: Webb has delivered the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe so far – and in only 12.5 hours.The next day, July 12, 2022, more images were released showing the capabilities of all four of Webb’s state-of-the-art scientific instruments: Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI | More about this image. The image shows the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 as it appeared 4.6 billion years ago. Webb's First Deep Field, taken by Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), is a composite made from images at different wavelengths, totaling 12.5 hours – achieving depths at infrared wavelengths beyond the Hubble Space Telescope’s deepest fields, which took weeks. Called Webb’s First Deep Field, the image shows galaxy cluster SMACS 0723, a cluster teeming with thousands of galaxies – including the faintest objects ever observed in the infrared. Joe Biden previewed the first full-color image from Webb – the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe so far. Webb's location gives it a wide view of the cosmos, and will keep the telescope's optics and scientific instruments cold enough to function and perform optimal science. And I can’t wait to see Webb’s first new views of the universe this summer!” We’re one step closer to uncovering the mysteries of the universe. “Congratulations to the team for all of their hard work ensuring Webb’s safe arrival at L2 today. “Webb, welcome home!” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. 24, 2022, the mission team fired Webb’s thrusters and inserted the space telescope into orbit around the Sun at the second Lagrange point, or L2, its final destination, nearly 1 million miles from Earth. “This is the first time a NASA-led mission has ever attempted to complete a complex sequence to unfold an observatory in space – a remarkable feat for our team, NASA, and the world.” Robinson, Webb program director at NASA Headquarters. “The successful completion of all of the Webb Space Telescope’s deployments is historic,” said Gregory L. 8, 2022, the Webb team fully deployed the telescope's 21-foot, gold-coated primary mirror, successfully completing the final stage of all major spacecraft deployments to prepare for science operations. The spacecraft separated from the rocket 27 minutes into the flight at an altitude of approximately 870 miles (1,400 kilometers). The James Webb Space Telescope is on its own after separating from the Arianespace Ariane 5 rocket that launched it into space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
